Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishii, Yui*; Yamamoto, Arisa*; Sato, Naoki*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ohara, Koji*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Mori, Takao*; Mori, Shigeo*
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134111_1 - 134111_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) C
CFukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nuclear Technology, 205(9), p.1154 - 1163, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:97.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)An electromagnetic-levitation technique performed in a static magnetic field was used to measure the density, surface tension, normal spectral emissivity, heat capacity, and thermal conductivity of molten 316L stainless steel (SS316L) and SS316L that contained 5mass%B C. The addition of 5mass%B
C. The addition of 5mass%B C to SS316L yielded reductions of 111 K, 6%, 19%, and 6% in the liquidus temperature, density, normal spectral emissivity, and thermal conductivity at the liquidus temperature of SS316L, respectively. The heat capacity increased by 5% with this addition. Although the 5mass%B
C to SS316L yielded reductions of 111 K, 6%, 19%, and 6% in the liquidus temperature, density, normal spectral emissivity, and thermal conductivity at the liquidus temperature of SS316L, respectively. The heat capacity increased by 5% with this addition. Although the 5mass%B C addition had no clear effect on the surface tension, sulfur dissolved in the SS316L resulted in a significant decrease in the surface tension.
C addition had no clear effect on the surface tension, sulfur dissolved in the SS316L resulted in a significant decrease in the surface tension.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.513 - 520, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study revealed melting points and thermal conductivities of four samples generated by sodium-concrete reaction (SCR). We prepared the samples using two methods such as firing mixtures of sodium and grinded concrete powder, and sampling depositions after the SCR experiments. In the former, the mixing ratios were determined from the past experiment. The latter simulated the more realistic conditions such as the temperature history and the distribution of Na and concrete. The thermogravimetry-differential thermal analyzer (TG-DTA) measurement showed the melting points were 865-942 C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840
C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840 C and the melting point was 840-850
C and the melting point was 840-850 C, which was 10-20
C, which was 10-20 C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na
C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na SiO
SiO and/or Na
and/or Na SiO
SiO . Moreover, the thermal conductivity was
. Moreover, the thermal conductivity was  =1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa
=1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa O-1-xSiO
O-1-xSiO (x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700
(x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700 C were explained by the equation of
C were explained by the equation of 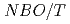 .
.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Saito, Kosuke; Uno, Masayoshi*
Nuclear Technology, 205(3), p.474 - 485, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study evaluated the effects of plutonium content and self-irradiation on the thermal conductivity of mixed-oxide (MOX) fuel. Samples of UO fuel and various MOX fuels were tested. The MOX fuels had a range of plutonium contents, and some samples were stored for 20 years. The thermal conductivity of these samples was determined from thermal diffusivity measurements taken via laser flash analysis. Although the thermal conductivity decreased with increasing plutonium content, this effect was slight. The effect of self-irradiation was investigated using the stored samples. The reduction in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation depended on the plutonium content, its isotopic composition, and storage time. The reduction in thermal conductivity over 20 years' storage can be predicted from the change of lattice parameter. In addition, the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation was recovered with heat treatment, and recovered almost completely at temperatures over 1200 K. From these evaluation results, we formulated an equation for thermal conductivity that is based on the classical phonon-transport model. This equation can predict the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel thermal conductivity by accounting for the influences of plutonium content and self-irradiation.
fuel and various MOX fuels were tested. The MOX fuels had a range of plutonium contents, and some samples were stored for 20 years. The thermal conductivity of these samples was determined from thermal diffusivity measurements taken via laser flash analysis. Although the thermal conductivity decreased with increasing plutonium content, this effect was slight. The effect of self-irradiation was investigated using the stored samples. The reduction in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation depended on the plutonium content, its isotopic composition, and storage time. The reduction in thermal conductivity over 20 years' storage can be predicted from the change of lattice parameter. In addition, the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation was recovered with heat treatment, and recovered almost completely at temperatures over 1200 K. From these evaluation results, we formulated an equation for thermal conductivity that is based on the classical phonon-transport model. This equation can predict the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel thermal conductivity by accounting for the influences of plutonium content and self-irradiation.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Takano, Masahide; Kurata, Masaki; Arita, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 464, p.270 - 274, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 TiO
TiO added with TiO
added with TiO
Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Takeshi*; Nashimoto, Makoto*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Dokiya, Masayuki*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*; Takahashi, Yoichi*
JAERI-Conf 2004-012, p.140 - 147, 2004/07
no abstracts in English
 TiO
TiO
Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Takeshi*; Nashimoto, Makoto*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*; Takahashi, Yoichi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, Supplement, Vol.112, No.1 (CD-ROM), p.S354 - S357, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
 Ti
TiUchida, Munenori*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Kawamura, Hiroshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 69(1-4), p.499 - 503, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 TiO
TiO pebble bed for a demo blanket
pebble bed for a demo blanketHatano, Toshihisa; Enoeda, Mikio; Suzuki, Satoshi; Kosaku, Yasuo; Akiba, Masato
Fusion Science and Technology, 44(1), p.94 - 98, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Shiina, Yasuaki; Inagaki, Terumi*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 69(681), p.1233 - 1241, 2003/05
In order to reduce phase change time in latent heat technology, improvement of effective thermal conductivity of heat storage unit would be one of the techniques. Effect of effective thermal conductivity on melting time are studied analytically of circular composite heat storage capsules made by immersing phase change materials (PCM) into porous metals. Numerical and approximate analysis were made with the consideration of uniform and non-uniform heat transfer coefficients around the cylindrical surface. Four PCMs (H O,Octadecane, Li
O,Octadecane, Li CO
CO , NaCl) and three metals (copper, aluminum and carbon steel) were selected specific materials. Porosity of the metals were restricted larger than 0.9 in order to lessen decrease in latent heat. Results show that reduction in melting time was obtained for the above PCMs, especially for low conductivity PCMs. Melting time obtained by approximate analysis agrees well with numerical analysis. High Nusselt number and high thermal conductivity of heat transfer fluid would be more effective to reduce phase change time.
, NaCl) and three metals (copper, aluminum and carbon steel) were selected specific materials. Porosity of the metals were restricted larger than 0.9 in order to lessen decrease in latent heat. Results show that reduction in melting time was obtained for the above PCMs, especially for low conductivity PCMs. Melting time obtained by approximate analysis agrees well with numerical analysis. High Nusselt number and high thermal conductivity of heat transfer fluid would be more effective to reduce phase change time.
Uemura, Takuya*; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Ichimiya, Koichi*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Yamanashi Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (020-4), p.49 - 50, 2002/10
A heat transfer experiment was performed using a horizontal circular tube to obtain the heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics in the tube inserted copper wire. From the results obtained in this experiment, it was found that an amount of heat removal in the tube with copper wire inserts increased about 20% comparing with a tube having a smooth wall. A heat transfer coefficient of the tube inserted copper wire also increased 30% to 50% under the constant pumping power condition.
Nakamura, Jinichi
Saishin Kaku Nenryo Kogaku; Kodoka No Genjo To Tembo, p.93 - 98, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Motoe
Saishin Kaku Nenryo Kogaku; Kodoka No Genjo To Tembo, p.131 - 140, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
; ; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TN9400 2000-109, 96 Pages, 2000/11
Numerical calculations were carried out for a free surface sloshing, a thermal stratification, a thermal striping, and a natural convection as key phenomena of in-vessel thermohydraulics in future fast reactor systems with various fluids as coolants. This numerical work was initiaied based on a recognition that the fundamental characteristics of the phenomena have been unsolved quantitatively in the use of various coolants. From the analysis for the phenomena, the following results were obtained. [Free Surface Sloshing phenomena] (1)Ther is no remarkable difference betweeen liquid sodium and luquid Pb-Bi in characteristics of internal flows and free surface charatristics based on Fr number. (2)the AQUA-VOF code has a potentiall enough to evaluate gas entrainment behavior from the free surface including the internal flow characteristics. [thermal Stratification Phenomena] (1)On-set position of thermal entainment process due to dynamic vortex flows was moved to downstream direction with decreasing of Ri number. 0n the other hand, the position in the case of C0 gas was shifted to upstream side with decreasing of Ri number. (2)Destruction speed of the thermal stratyification interface was dependent on thermal diffusivity as fluid properties. therefor it was concluded that an elimination method is necessary for the interface generated in C0
gas was shifted to upstream side with decreasing of Ri number. (2)Destruction speed of the thermal stratyification interface was dependent on thermal diffusivity as fluid properties. therefor it was concluded that an elimination method is necessary for the interface generated in C0 gas. [thermal Striping Phenomena] (1)Large amplitudes of fluid temperature fluctuations was reached to down stream area in the use of CO
gas. [thermal Striping Phenomena] (1)Large amplitudes of fluid temperature fluctuations was reached to down stream area in the use of CO gas, due to larger fluid viscosity and smaller thermal diffusivity, compared with liquid sodium and liquid Pb-Bi cases. (2)To simulate thermal striping conditions such as amplitude and frequency of the fluid temperature fluctuations, it isnecessary for coincidences of Re number for the amplitude and of velocity value for the frequency, in various coolants. [Natural Convection Phenomena] (1)Fundamental behavior of the natural convection in various coolant follows buoyant jet ....
gas, due to larger fluid viscosity and smaller thermal diffusivity, compared with liquid sodium and liquid Pb-Bi cases. (2)To simulate thermal striping conditions such as amplitude and frequency of the fluid temperature fluctuations, it isnecessary for coincidences of Re number for the amplitude and of velocity value for the frequency, in various coolants. [Natural Convection Phenomena] (1)Fundamental behavior of the natural convection in various coolant follows buoyant jet ....
Tejima, Shogo
JNC TN8400 2000-029, 54 Pages, 2000/10
This report describes the study done by the author as a postdoctoral research associate at Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. This report is divided into three parts: construction of a relativistic band calculation formalism based on the density functional theory, using this method, investigation of the electrical properties for ferromagnetic UGe and antiferromagnetic UO
and antiferromagnetic UO . (1)A relativistic band calculation (RBC) method. Band calculations for the s, p, and d electric structure have been developed well in the practical application and theoretical study. But band calculation method treating magnetic 5f electrons as actinide compounds are complicated and needed relativistic approach, so it is behind with the study of the 5f system. In this study we construct the relativistic band calculationformalism valid for magnetic 5f electrons. (2)Electric properties of UGe
. (1)A relativistic band calculation (RBC) method. Band calculations for the s, p, and d electric structure have been developed well in the practical application and theoretical study. But band calculation method treating magnetic 5f electrons as actinide compounds are complicated and needed relativistic approach, so it is behind with the study of the 5f system. In this study we construct the relativistic band calculationformalism valid for magnetic 5f electrons. (2)Electric properties of UGe . The actinide compounds UGe
. The actinide compounds UGe is ferromagnetic, so the theoretical analysis is not well yet. The electric structure and fermi surface of UGe
is ferromagnetic, so the theoretical analysis is not well yet. The electric structure and fermi surface of UGe are analyzed using the RBC. The theoretical results show that UGe
are analyzed using the RBC. The theoretical results show that UGe is heavy electron with the 5f character and are agreement with experimental one. (3)Electric structure of nuclear fuel UO
is heavy electron with the 5f character and are agreement with experimental one. (3)Electric structure of nuclear fuel UO . It is important to understand the mechanism of the thermal conductivity of nuclear fuel as antiferromagnetic UO
. It is important to understand the mechanism of the thermal conductivity of nuclear fuel as antiferromagnetic UO . The UO
. The UO band calculation reflecting the thermal properties, into account of relativistic effect, have not done yes. So using the RBC the detailed electric structure of UO
band calculation reflecting the thermal properties, into account of relativistic effect, have not done yes. So using the RBC the detailed electric structure of UO are obtained.
are obtained.
Mizuta, Shunji; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-048, 28 Pages, 2000/04
ODS (Oxide Dispersion Strengthened) ferritic-martainsitic steels are one of the most prospective cladding materials for advanced fast breeder reactors, since they are expected to have excellent swelling resistance and superior high temperature strength due to the finely distributed stable oxide particles(Y O
O ). Properties and the tentative strength equations for ODS ferritic-martainsitic were proposed on the basis of the latest data to apply to the feasibility study of the sodium coolant MOX fuel plant. The items of equations are follows. (1)creep rupture strength (2)correction factor of creep rupture strength (in Na and in reactor) (3)outer surface eorrosion (Na) (4)inner surface corrosion (in MOX fuel pin) (5)thermal conductivity
). Properties and the tentative strength equations for ODS ferritic-martainsitic were proposed on the basis of the latest data to apply to the feasibility study of the sodium coolant MOX fuel plant. The items of equations are follows. (1)creep rupture strength (2)correction factor of creep rupture strength (in Na and in reactor) (3)outer surface eorrosion (Na) (4)inner surface corrosion (in MOX fuel pin) (5)thermal conductivity
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; *; Okano, Yasushi; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TY9400 2000-012, 91 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Yamanaka, Shinsuke*; Uno, Masayoshi*; Kurosaki, Ken*; ; Namekawa, Takashi
JNC TY9400 2000-011, 41 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Yamanaka, Shinsuke*; Abe, Kazuyuki
JNC TY9400 2000-004, 78 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
; kasahara, Naoto; ; ; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TN9400 2000-010, 168 Pages, 2000/02
Thermal striping is significant issue of the structural integrity, where the hot and cold fluids give high cycle fatigue to the structure through the thermal stress resulted from the time change of temperatur distibution in the structure. In the sodium cooled fast reactor, temperature change in fluid easily transfers to the structure because of the high thermal conductivity of the sodium. It means that we have to take care of thermal striping, The thermal striping is complex phenomena between the fluid and structure engineering fields. The investigations of thermal striping are not enough to evaluate the integrity directly. That is the fluctuation intensity at the structure surface is assumed to be temperature difference between source fluids (upstream to the mixing region) as the maximum value in the design. 0therwise, the design conditions are defined by using a mockup experiment and large margin of temperature fluctuation intensity. Furthermore, such evaluation manners have not yet been considered as a design rule. Transfer mechanism of temperature fluctuation from fluid to structure has been investigated by the authors on the view points of the fluid and structure. Attenuation of temperature fluctuation was recognized as a dominant factor of thermal fatigue. We have devdoped a numerical analysis system which can evaluate thermal fatigue and crack growth with consideration of the attenuation of temperature fluctuation in fluid, heat transfer, and structure. This system was applied to a real reactor and the applicability was confirmed. Further verification is planned to generalize the system. For the higher cost performance of the fast reactor, an evaluation rule is needed, which can estimate thermal loading with attenuation and can be applied to the design. An idea of the rule is proposed here. Two methods should be prepared; one is a precise evaluation method where mechanism of attenuation is modeled, and the other is simple evaluation method where ...